As I have noted elsewhere, Gilbert N. Lewis wrote a famous paper entitled “the atom and the molecule“, the centenary of which is coming up.[1] In a short and rarely commented upon remark, he speculates about the shared electron pair structure of acetylene, R-X≡X-R (R=H, X=C). It could, he suggests, take up three forms. H-C:::C-H and two more which I show as he drew them. The first of these would now be called a bis-carbene and the second a biradical.
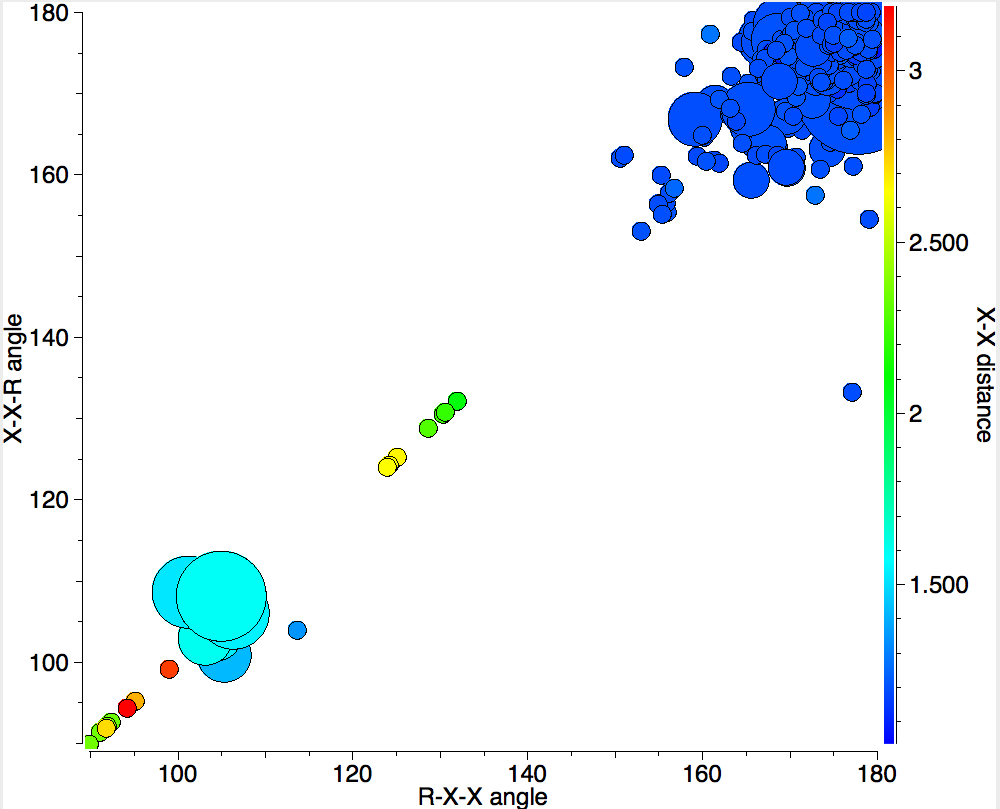
In 1916, it was too early for Lewis to speculate what the geometries of such species might be, and in particular the C…C (or generalising, X…X) distance, and the two angles, one for each X. Well, we do not need to speculate, we can perform a search of the crystal structure database. Here it is (R < 0.05, no errors, no disorder):
A little more explanation of this 4-dimensional plot is needed:
- The two angles are plotted as X and Y.
- The X…X distance is plotted as colour, with red representing the longest distances and blue the shortest
- The size of each “bin” is represented by the radius of the circle; small circles represent few examples, larger circles represent more examples in each “bin” defined by a regular range of angles.
There are one or two off-diagonal “outliers”, each of which probably deserves individual inspection. But dealing just with the obvious clusters, the overwhelmingly largest is for both angles of ~180°, and these are the triple bonds we know and love. As far as I know, Lewis was the first to propose a triple bond between two atoms, but if anyone reading this blog knows of an antecedent, do let me know. The next cluster is for angles of ~109° and these are clearly bis-carbenes. These all occur when X ≠ C. There are two small clusters worthy of note; one ~130° and one ~90°. The latter are mostly Pb-Pb and Sn-Sn, where the bonding is unhybridised pure p.
One of the limitations of searching for crystal structures is that the spin state of each molecule is never given. The biradical structure given by Lewis could well have a triplet ground state, and perhaps that might have very characteristic angles (~130° ?). It would be great to identify a genuine example of this biradical form!
As usual, the search itself took around 10 minutes, and it provides much interesting food for thought; not bad for a 100-year-old idea!
Acknowledgments
This post has been cross-posted in PDF format at Authorea.
References
- G.N. Lewis, "THE ATOM AND THE MOLECULE.", Journal of the American Chemical Society, vol. 38, pp. 762-785, 1916. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja02261a002
Tags: Carbene, Carbenes, Chemistry, Cluster chemistry, food, Functional groups, Gilbert N. Lewis, Non-Kekulé molecule, Organic chemistry, Organic compounds
This structure looked a possibility for Lewis' Si::Si middle form: doi: 10.5517/CC87H32. However, a calculation reveals the Wiberg Si=Si bond order is 2.57 and the NBO-1, although distorted very much according to the Lewis idea, is still firmly spin-paired into a singlet spin state (doi: 10.14469/ch/191836) A related structure is doi: 10.5517/CCY1357
The Pb-Pb analogue is an unknown molecule, its calculated Wiberg bond order is 1.57 (length 2.81Å) and the C-Pb-Pb bond angle is 122.2°.
But another Pb-Pb compound is known (QIMQUY, doi: 10.1021/ja993346m) where the C-Pb-Pb angle is reported as 94.3° and the Pb-Pb length is 3.19Å. This dramatic difference between the two forms suggests that Pb compounds might be capable of existing in two valence-bond isomeric forms, each corresponding to one of Lewis' forms. Watch this space.