This post, the fifth in the series, comes full circle. I started off by speculating how to invert the stereochemical outcome of an electrocyclic reaction by inverting a bond polarity. This led to finding transition states for BOTH outcomes with suitable substitution, and then seeking other examples. Migration in homotropylium cation was one such, with the “allowed/retention” transition state proving a (little) lower in activation energy than the “forbidden/inversion” path. Here, I show that with two electrons less, the stereochemical route indeed inverts. First, a [1,4] alkyl shift with inversion at the migrating carbon (ωB97XD/6-311G(d,p)/SCRF=chloroform); as a four-electron process, this is the “allowed” route.[1]
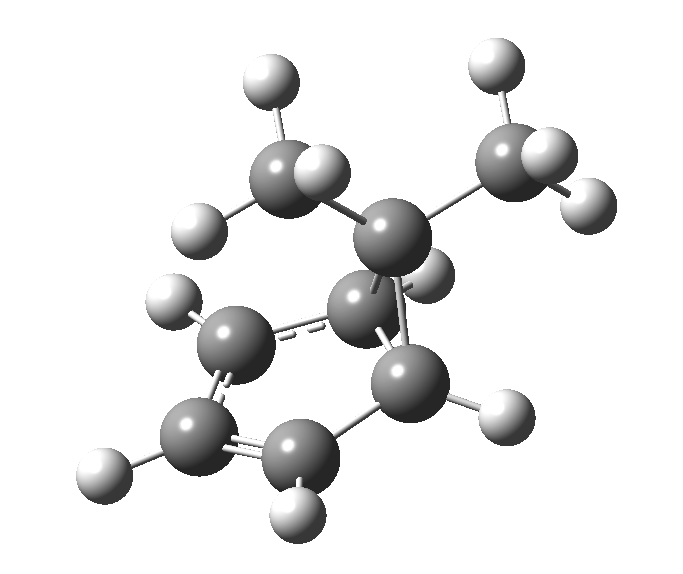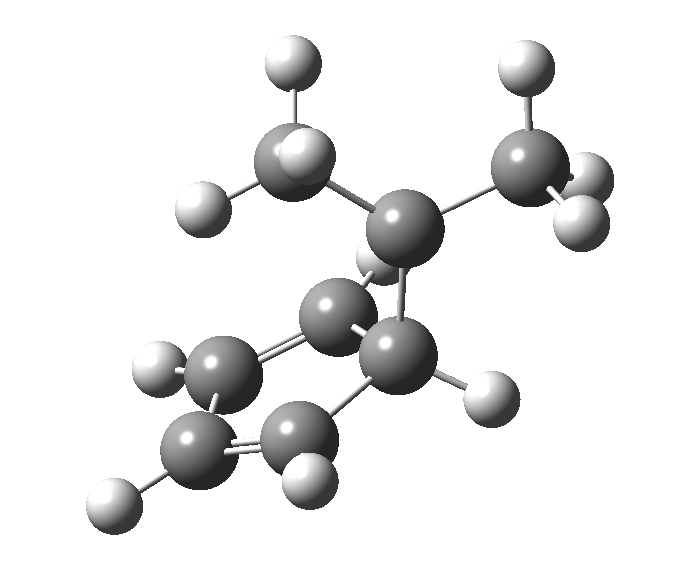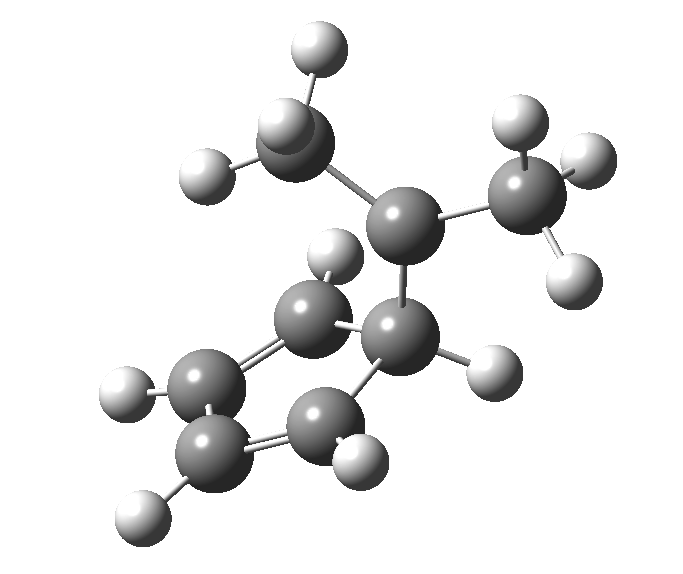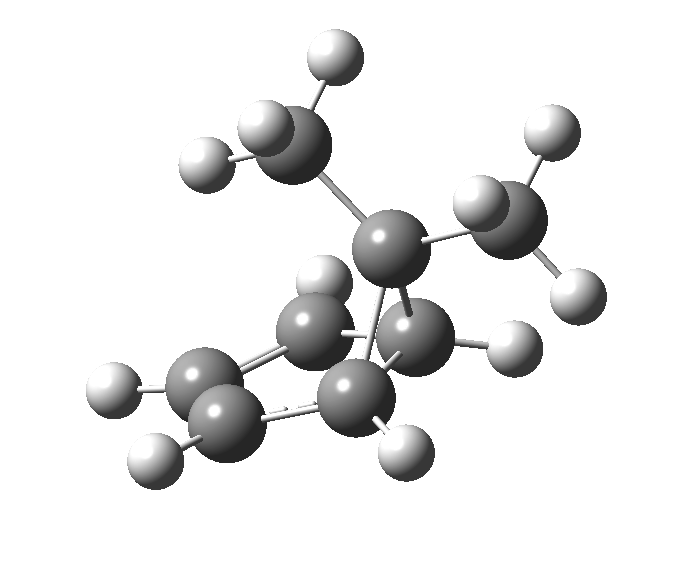 The “forbidden” route corresponds to retention of configuration at the migrating carbon.[2]
The “forbidden” route corresponds to retention of configuration at the migrating carbon.[2] 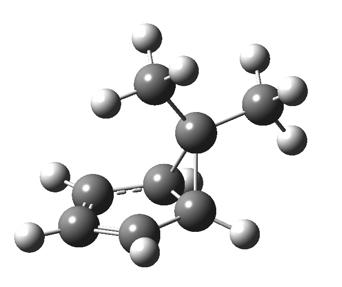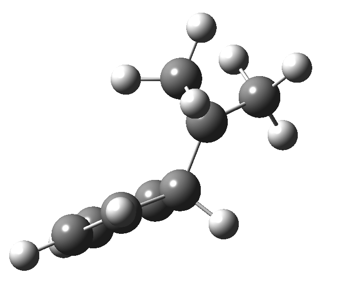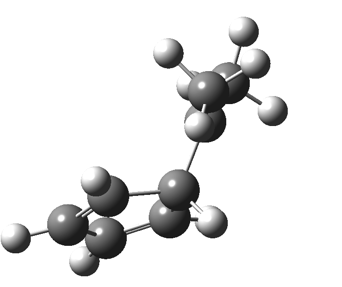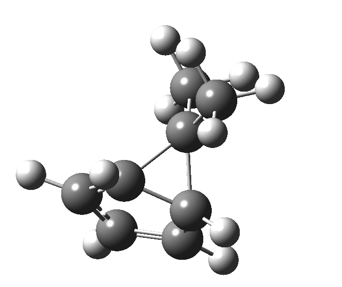 The barriers for each process can be seen below from the IRCs. That for inversion is ~4.5 kcal/mol lower than retention. This nicely transposes the values for the six-electron homologue shown in the previous post.
The barriers for each process can be seen below from the IRCs. That for inversion is ~4.5 kcal/mol lower than retention. This nicely transposes the values for the six-electron homologue shown in the previous post. There is one more nugget of insight that can be extracted. The start/end-point for the six-electron process (homotropylium cation) was, as the name implies, homoaromatic. Now, with a four-electron system we also have an inverse. Nominally, we should now end with homo-antiaromaticity (but see [3]). But antiaromaticity is avoided whenever possible, and so the homoaromatic bond observed in homotropylium is not formed. It resolutely remains a σ-bond (1.48Å) thus sequestering two electrons, and the remaining two electrons simply form a delocalised allyl cation. With the six-electron homotropylium, reactant/product were stabilised by that additional (homo)aromaticity, thus inducing a relatively high barrier. With the four-electron system here, no such reactant/product stabilisation occurs, and hence the reaction barriers are now significantly lower. A rather neat pedagogic example.
References
- H.S. Rzepa, "Gaussian Job Archive for C8H11(1+)", 2014. https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.1142175
- H.S. Rzepa, "Gaussian Job Archive for C8H11(1+)", 2014. https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.1142174
- C.S.M. Allan, and H.S. Rzepa, "Chiral Aromaticities. A Topological Exploration of Möbius Homoaromaticity", Journal of Chemical Theory and Computation, vol. 4, pp. 1841-1848, 2008. https://doi.org/10.1021/ct8001915